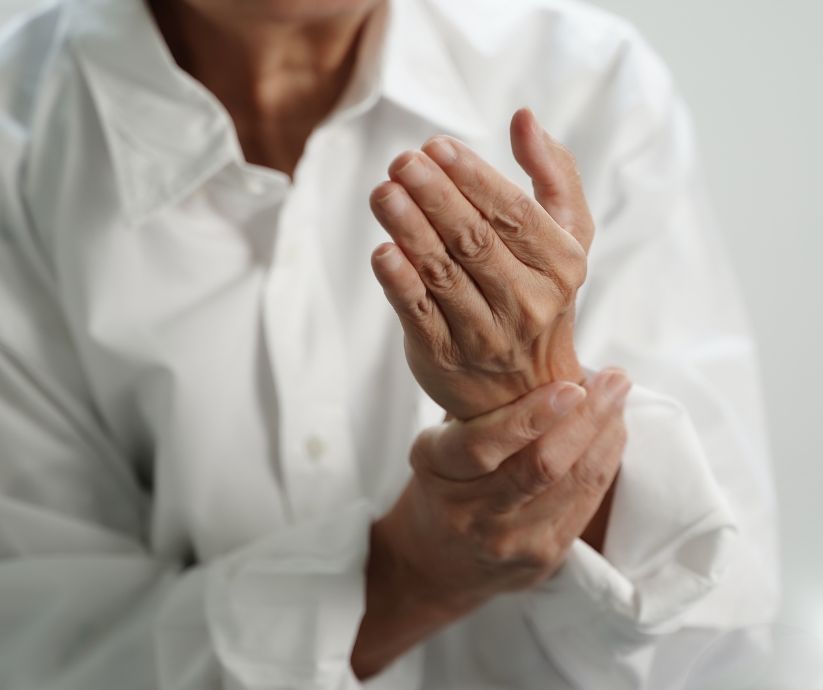
Early changes in the gut microbiome may offer a window for preventive treatments in rheumatoid arthritis.
New research reveals that shifts in gut bacteria months before the onset of rheumatoid arthritis could enable preventative interventions.
Changes in the gut microbiome appear up to ten months before clinical rheumatoid arthritis develops, potentially creating an early intervention point for preventive treatments, according to a study published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Conducted by the University of Leeds, this longitudinal study tracked 19 individuals at high risk of rheumatoid arthritis, finding that those who progressed to the disease showed higher levels of inflammatory bacteria like Prevotella months before symptoms emerged.
Researchers found that while some patients showed gut instability, others with stable microbiomes did not progress to clinical arthritis. This finding opens the door to early preventive strategies such as dietary changes, prebiotics, probiotics, and even improved dental hygiene to reduce harmful gut bacteria.
“This research highlights the profound connection between gut health and systemic inflammation, reinforcing what many in naturopathic medicine have long observed. The discovery that shifts in gut bacteria can precede rheumatoid arthritis by several months opens a window for early intervention. By focusing on gut health through targeted dietary changes, probiotics, prebiotics, and lifestyle adjustments, we may be able to reduce inflammation and potentially prevent the onset of this debilitating condition.” – Elizabeth Taddiken, ND Dr. Elizabeth Taddiken | Rockwood Natural Medicine Clinic
Reference: Rooney CM, Jeffery IB, Mankia K, Wilcox MH, Emery P. Dynamics of the gut microbiome in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024; ard-2024-226362. doi:10.1136/ard-2024-226362
See Also:
Antibiotics Linked to Increased Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis